Multi-factor authentication
Two-factor authentication further developed – Modern authentication methods for more security
What is multi-factor authentication and
why is cidaas the ideal solution?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) has become one of the most important tools for protecting data. Last but not least, media attention has ensured that multi-factor authentication has almost become the standard for companies and is increasingly replacing logging in with (just) one password. With multi-factor authentication, at least two different factors from the categories of knowledge, possession and inherence are used for strong authentication. In addition to outdated authentication options such as passwords or security questions, common factors include confirmation codes via SMS or email, one-time passwords or authentication with biometric features such as facial scans. The decisive factors for successful multi-factor authentication are the authentication methods offered and when multi-factor authentication makes sense. Otherwise, it can quickly be perceived as annoying and inconvenient.
What is the difference between multi-factor authentication and two-factor authentication?
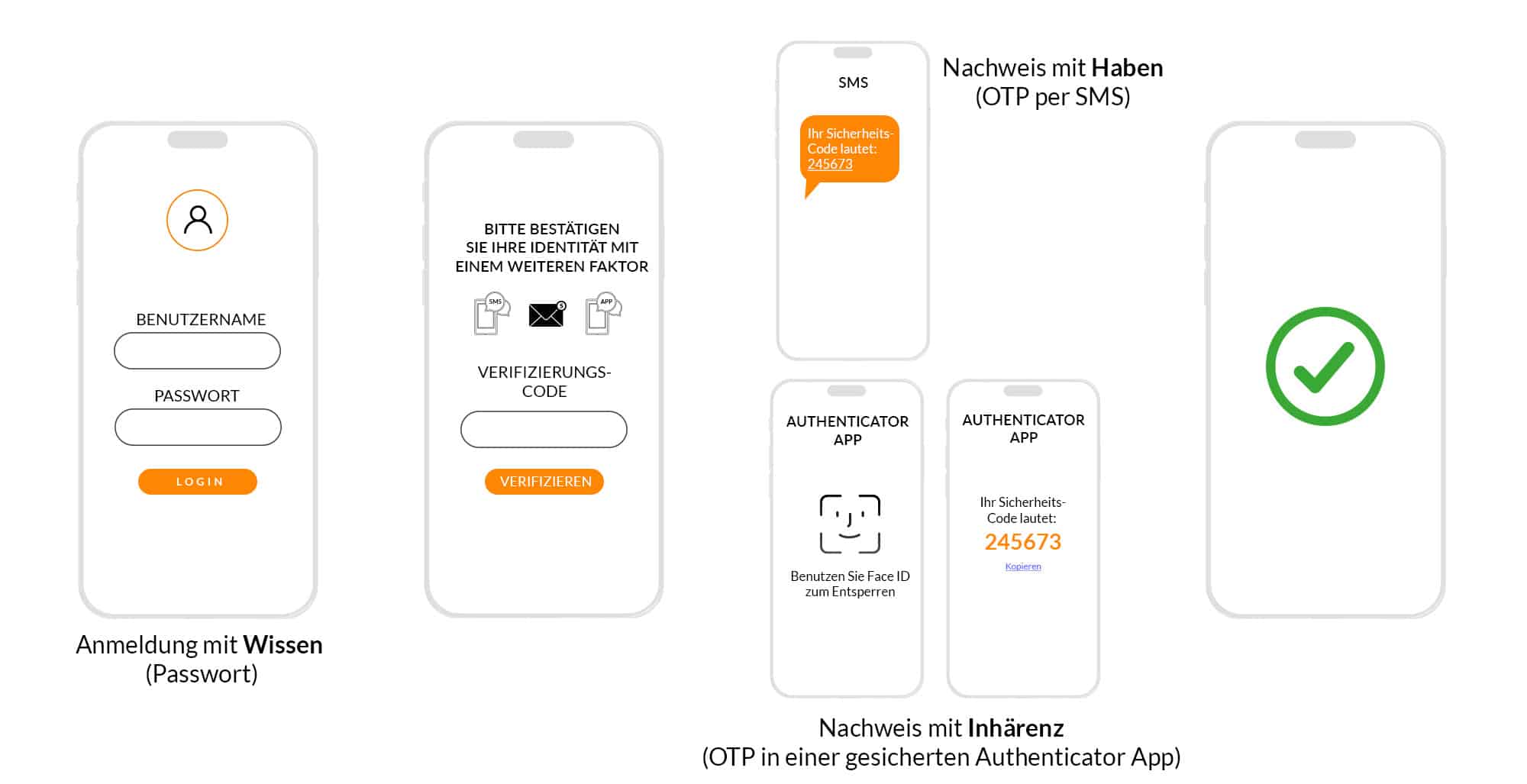
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) or its specialized form, two-factor authentication (2FA), are methods used to increase the security of online platforms by ensuring that a user proves their identity in more than one way.
Multi-factor authentication is a broad term and refers to any authentication method that uses more than one factor for identity verification. Often there are at least three factors. An MFA can be a combination of something the user knows (knowledge), has (possession) and is (inherence), as well as other biometric factors. Each factor increases security.
2FA is a special form of MFA and, as the name suggests, requires two different factors for identity verification. Each factor is a self-contained component of authentication and can be classified into one of the following categories: Knowledge, Possession and Inherence (Biometrics).
Compared to 2FA, MFA usually offers more flexibility and security by using more than 2 factors for identity verification.The choice between MFA or 2FA depends on the specific requirements and the available resources.
MFA case study:
If you consider a website login with user name and password, as well as an additional code by email as a one-time password or one-time password (OTP), this is a classic two-factor authentication. However, if you use a different method instead of an email OTP, e.g. a push OTP in an app on the smartphone, and additionally protect this app with device biometrics (e.g. facial recognition or fingerprint), the security level increases.


Such a combination of different authentication methods is often used to create multi-factor authentication in banking apps. TAN, PIN and bank card are among the most common authentication factors for online banking.
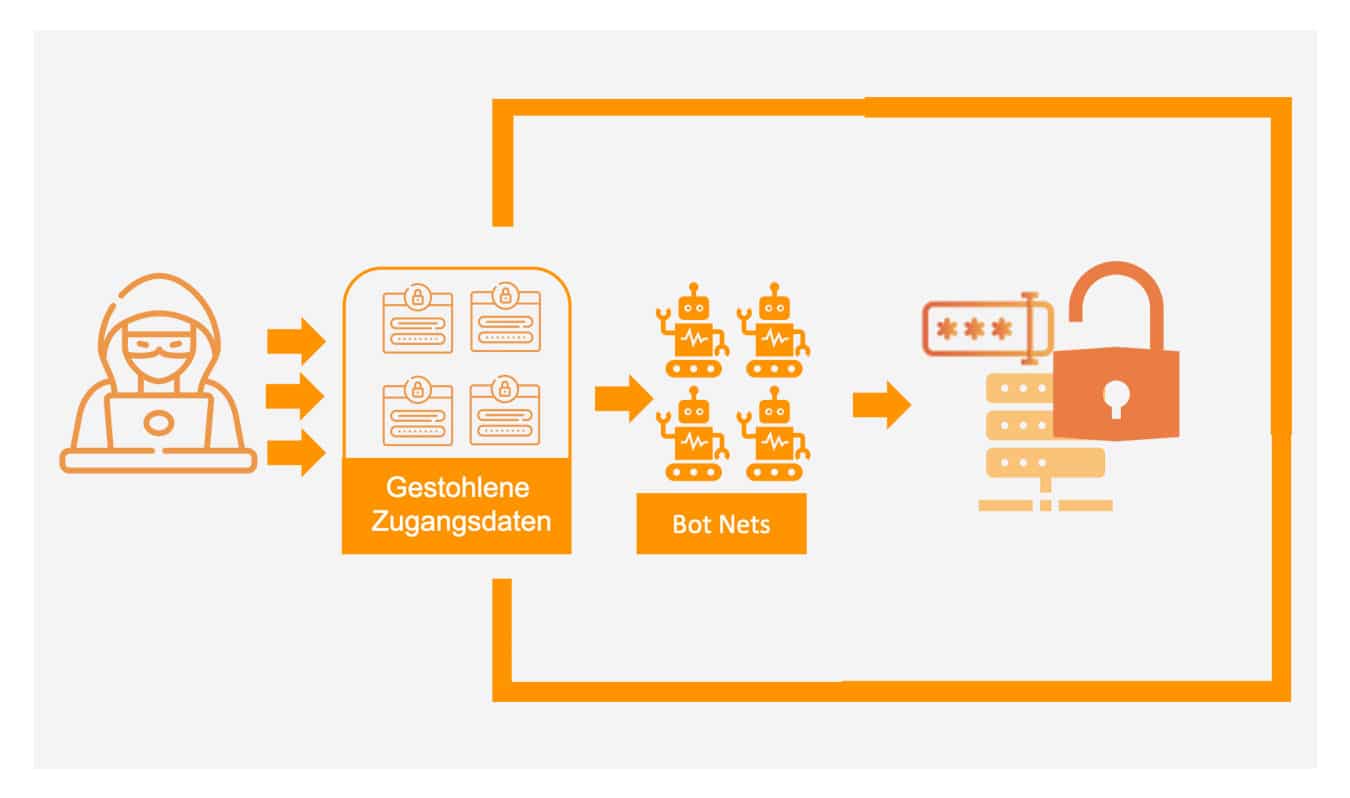
Protection against identity theft
Protect your customers with smart MFA & the fraud and bot net detection integrated in cidaas.
User comfort
Inspire your users with convenient login procedures that allow them to select procedures independently.
Security & flexibility
Use cidaas to specify which authentication methods you want to allow for each application.
Why multi-factor authentication?
cidaas provides protection against identity theft and fraud detection through multi-factor authentication, while allowing flexibility in the choice of authentication methods and customization to individual needs. This increases security and user convenience by simultaneously promoting convenient login procedures and the avoidance of weak passwords.
Advantages & benefits of
multi-factor authentication

Identity theft protection with smart MFA
Identity theft is a constant threat to users. Criminals are constantly finding new ways to manipulate data and misuse it. Every company is therefore a direct target of cybercrime. In addition to financial losses, hacked accounts also result in reputational damage – for example, if sensitive customer data is disclosed. With a smart MFA and the fraud and botnet detection integrated in cidaas, you can protect your customers and offer an option for verifying user identity. With the smart MFA, multi-factor authentication can be added automatically on a context-specific basis, in this case in the event of suspicious behavior.
Security and flexibility
A second factor initially stands for more security. However, it usually also involves additional work. With cidaas, you can decide how authentication should look – individually, according to your needs.
Strong authentication may not be necessary or useful for every access.Instead, specify which authentication methods you want to allow for each application.This already creates the first level of security. For example, a simple confirmation method is sufficient when logging in again on a device with the same account. If additional authentication is required for certain activities, you can add event-related multi-factor authentication. In addition, cidaas detects suspicious behavior so that the user only has to verify their identity via an additional factor in the event of suspicion.


User comfort
With cidaas smart multi-factor authentication, you can strengthen your security as required. Inspire your users with convenient login procedures that allow them to select their preferred method independently. cidaas offers a total of 4 different, modern authentication procedures that can be combined as required. This eliminates the security risk of weak or reused passwords.
Passwordless authentication procedures are another option for a modern login.
With cidaas you combine security with user convenience. Find out more about single sign-on and how it takes security and convenience to a new level.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is multi-factor authentication?
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) means that a user identifies themselves using another factor in addition to logging in with a factor such as their username. This enables them to verify their identity. Each factor can be assigned to one of three categories: knowledge, possession or inherence (biometrics). For optimum protection, one factor from each category should be used. An example of the knowledge factor is the password. With multi-factor authentication, at least one other authentication factor is required in addition to the password. An example of implicit multi-factor authentication is TouchID. TouchID requires a device with a fingerprint scanner (possession) and a fingerprint (biometrics), which is used to confirm the identity. This shows that With the right login procedures, secure multi-factor authentication can be passwordless and particularly convenient.
What is smart multi-factor authentication?
Smart multi-factor authentication means that an additional factor is only requested if it is necessary due to the situation or context. With intelligent fraud detection, for example, a second factor can only be requested in the event of suspicion.
What does strong customer authentication mean?
The term strong customer authentication is primarily a regulatory requirement and is coined by BaFin. It is understood to mean authentication that consists of at least two elements from two different categories (knowledge, possession and inherence/biometrics). The EBA (European Banking Authority) specifies which procedures are classified as SCA (Strong Customer Authentication). Among other things, it explicitly states that the classification as SCA depends on the implemented approach of the authentication procedure.
What is the difference between multi-factor authentication and two-factor authentication?
Two-factor authentication consists of two different factors. One factor is a component of authentication. It can be assigned to one of the following categories: Knowledge, possession and inherence (biometrics). Two-factor authentication is a special case of multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA requires at least two factors to verify identification.


cidaas - Cloud Identity & Access Management (Cloud IAM)
- Focus on user-friendly management of digital identities in any form
- Unique, secure user experience with modern 2-factor authentication
- GDPR-compliant, customizable consent management